|
|
1. General points
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
You will also find your CPSC340 textbook useful for this stage. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
3. Input to build your scanner Tokens: Special symbols : + - * / < <= > >= == != = ; , ( ) [ ] { } /* */ Keywords : else if int return void while Identifiers : ID = letter letter* letter = a|..|z|A|..|Z Numerals : NUM = digit digit* digit = 0|1|...|9 Note :
4. Token standard
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
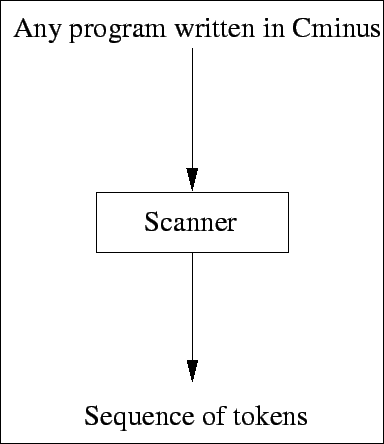
5. Scanner I/O structure
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Program nfact.mns [EFS]>cat nfact.mns
/**************
recursive N factorial. Used
for testing recursion. Also
used to make sure that the
answer from recursive n! is the
same as iterative n!.
**************/
/* recursively call n!*/
int nfact(int n)
{
if( n == 0 )
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return(n*nfact(n-1));
}
return 0;
}
void main(void)
{
int n;
n = input();
n = nfact(n);
output(n);
}
[EFS]>
Example #1 [EFS]>cminus nfact.mns
CMINUS COMPILATION: nfact.mns
IN NO PARSE
10: reserved word: int
10: ID, name= nfact
10: (
10: reserved word: int
10: ID, name= n
10: )
11: {
12: reserved word: if
12: (
12: ID, name= n
12: ==
12: NUM, val= 0
12: )
13: {
14: reserved word: return
14: NUM, val= 1
14: ;
15: }
16: reserved word: else
17: {
18: reserved word: return
18: (
18: ID, name= n
18: *
18: ID, name= nfact
18: (
18: ID, name= n
18: -
18: NUM, val= 1
18: )
18: )
18: ;
19: }
21: reserved word: return
21: NUM, val= 0
21: ;
22: }
24: reserved word: void
24: ID, name= main
24: (
24: reserved word: void
24: )
25: {
26: reserved word: int
26: ID, name= n
26: ;
27: ID, name= n
27: =
27: ID, name= input
27: (
27: )
27: ;
28: ID, name= n
28: =
28: ID, name= nfact
28: (
28: ID, name= n
28: )
28: ;
29: ID, name= output
29: (
29: ID, name= n
29: )
29: ;
30: }
31: EOF
[EFS]>
Example #2 [EFS]>c- nfact.mns
*********C- COMPILATION: nfact.mns*********
Scanning the source file...
10: reserved word: int
10: ID, name= nfact
10: (
10: reserved word: int
10: ID, name= n
10: )
11: {
12: reserved word: if
12: (
12: ID, name= n
12: ==
12: NUM, val= 0
12: )
13: {
14: reserved word: return
14: NUM, val= 1
14: ;
15: }
16: reserved word: else
17: {
18: reserved word: return
18: (
18: ID, name= n
18: *
18: ID, name= nfact
18: (
18: ID, name= n
18: -
18: NUM, val= 1
18: )
18: )
18: ;
19: }
21: reserved word: return
21: NUM, val= 0
21: ;
22: }
24: reserved word: void
24: ID, name= main
24: (
24: reserved word: void
24: )
25: {
26: reserved word: int
26: ID, name= n
26: ;
27: ID, name= n
27: =
27: ID, name= input
27: (
27: )
27: ;
28: ID, name= n
28: =
28: ID, name= nfact
28: (
28: ID, name= n
28: )
28: ;
29: ID, name= output
29: (
29: ID, name= n
29: )
29: ;
30: }
31: End of File
[EFS]>
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
7. What to hand in
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
8. Scanner Testing The test code will only be made available after this part of the project has been marked, so that you can correct your code. It is your responsibility to develop your own tests and make sure this part of the project works. Note that you do not submit tests that you create yourself. Scanner Tests (this link is only made active after you this part of the project has been marked) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||